The Easiest Ways to Stay On Top of Diabetes
Karly Hurley
| 4 min read
Did you know that diabetes is the leading cause of new vision loss and kidney disease in adults? If you or a loved one have diabetes, it can be overwhelming to think about. As anyone who has been diagnosed with diabetes knows, successfully managing the disease depends on regular monitoring and careful planning. That’s why one of the best things you can do is create a proactive monitoring plan – something that will work for you and your lifestyle. Your personal plan should be developed with your primary care team and will likely involve seeing how different factors such as diet and exercise affect your health. But it can be overwhelming to think about tracking things like what you eat, how often you go to the gym and blood sugar levels. Don’t get too stressed: these tips will make staying on top of your diabetes feel a lot more manageable:
Step 1: Make Sure to Get Regular Check-Ups
Schedule an appointment with your primary care physician every three to six months for a basic wellness check-up. Your physician will be able to help you re-evaluate your diabetes treatment plan and determine if you need further care. Make sure all of your shots are up to date, including flu and pneumonia; and ask for the following tests so you can keep tabs on your health:
- Hemoglobin Test (HbA1c): The A1C test is a simple blood test that measures your average blood sugar levels over a three-month period. It’s one of the most used tests to diagnose prediabetes and diabetes. It’s also the main test to help you and your health care team manage your diabetes. Higher A1C levels are linked to diabetes complications, so reaching and maintaining your individual A1C goal is very important if you have diabetes.
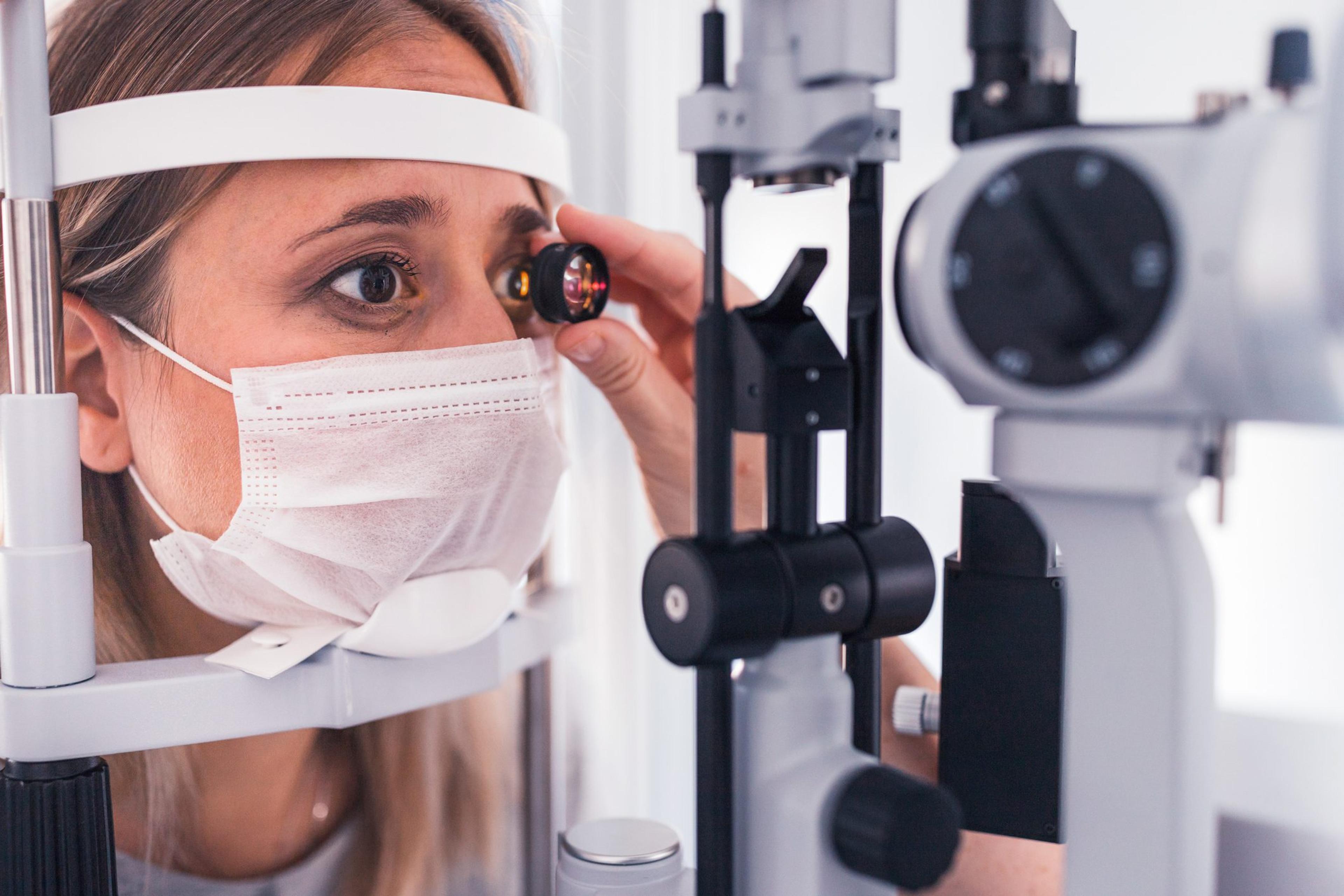
- Retinal eye exam: High blood sugar damages the walls of the small blood vessels in the eye, altering their structure and function. Routine screening offers the best hope for early detection of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetic retinopathy cannot be seen during a basic eye exam and require special exams. To get a better look at the inside of the eye, your eye doctor might administer drops to dilate your pupils.
- Blood pressure: Managing blood pressure is important for preventing long-term complications for individuals with diabetes.
- Total cholesterol (HDL, LDL, triglycerides): Diabetes tends to lower "good" cholesterol levels and raise "bad" cholesterol levels, which increases the risk for heart disease and stroke.
- Dental exam: Treating gum disease can help improve blood sugar control in patients living with diabetes, decreasing the progression of the disease. Practicing good oral hygiene and having professional deep cleanings done by your dentist can help to lower your HbA1c.
- Any other needed tests that your doctor recommends
Step 2: Become a Master at Monitoring
- Diet: It’s important to cut down on things that can cause blood sugar to spike, like refined carbs and added sugars. It is also very important to know which foods have carbohydrates, how to portion control them appropriately and spread them out evenly amongst meals for carbohydrate consistency. Keeping a food log (either in a little notebook or through an app on your phone) can help you track your diet. You’ll be able to pinpoint the connection between what you eat, when you ate, and spikes or dips in blood sugar.
- Exercise: Aim to get at least 30 minutes of exercise at least 5 days a week and talk to your primary care physician about what kind of workouts are right for you. Record your exercise using a wearable fitness tracker or app on your phone.
- Blood sugar levels: It’s important to keep a close eye on blood sugar levels because if your levels become too high, it can damage your heart, kidneys, feet and even eyes. Test your blood sugar at as prescribed by your primary care physician and record your numbers in a journal for future reference.
- Medicine: If you’re taking multiple medications, keep a detailed list of everything you are prescribed and share it with family members in case of an emergency. While you’re at it, make a checklist so you can mark off when you’ve taken your doses every day.
Step 3: Use the Blue Cross Mobile App
The Blue Cross Blue Shield of Michigan mobile app isn’t just useful for helping you track your payments and find a doctor, it’s also a way to sync all of your diabetes tracking information in one place. Use the “Health & Wellness” section of the app to sync your food journal, exercise tracker, blood sugar log and more. For more information about the prevention and management of diabetes, visit the American Diabetes Association or the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. More from MIBluesPerspectives:
Photo credit: Getty Images